Chapter 6 - Energy Sustainability
Part 3 - Electricity: Transmission, Distribution and Economics
Delivering Electricity to End Users
Summary: Smart-Grid: A Game-Changing Technology
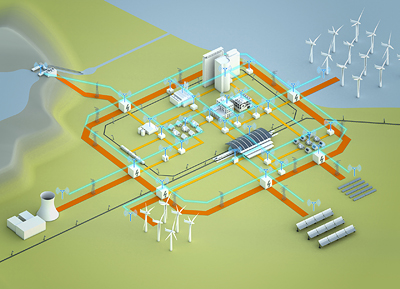
To summarize, a smart grid is “an automated, widely distributed energy delivery network, characterized by a two-way flow of electricity and information, capable of monitoring everything from power plants to customer preferences to individual appliances”. It “incorporates the benefits of distributed computing and communications into the grid to deliver real-time information and enable the near-instantaneous balance of supply and demand at the device level”.
Capabilities of a Smart Grid:
- Enables informed participation by consumers in retail and wholesale electricity markets
- Enables new products, services and markets
- Enhances integration of renewables
- Accommodates distributed electric generation and energy storage
- Provides for power quality for a range of needs by all types of consumers
- Optimizes asset utilization and operating efficiencies of the electric power system
- Anticipates and responds to system disturbances
- Operates resiliently to cyber/man-made attacks and natural disasters.
Part 3 - Electricity: Transmission, Distribution and Economics
Delivering Electricity to End Users
A. Basic Structure of Electric Power System
B. Transformer Basics and Losses
C. Transmission Lines and Grid Operations
D. Environmental, Health and Safety Issues – T&D
E. System Losses Weigh Heavily on Electricity Systems in Developing Countries
F. A Revolution in the Electricity Sector?
G. Small-Scale Power: Distributed Generation
Summary: Smart-Grid: A Game-Changing Technology
Electricity Markets and the Future of Electricity (NEXT)
(Adapted from the Energy Resources lecture materials of Jane Woodward, Consulting Associate Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Karl Knapp, Lecturer of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Stanford University by Cheryl Chadwick/Gregory Möller)
(Image credit: Siemens AG)

