Rapid Compression Expansion Machine (RCEM)
We have recently developed a rapid compression expansion machine (RCEM) which is being used to track the time evolution of reactive species during the autoignition process. The RCM apparatus mimics a single compression stroke of a reciprocating internal combustion engine. A fixed mass of premixed fuel-air mixture is brought to an elevated pressure and temperature condition at the compression top dead center, starting from initial conditions corresponding to a charge at much lower pressure and temperature. This machine permits time-resolved speciation using rapid quench of reacting products with a high degree of repeatability and precision timing. The understanding of autoignition chemistry for real fuels can provide insights into the development of the corresponding comprehensive reaction mechanisms.
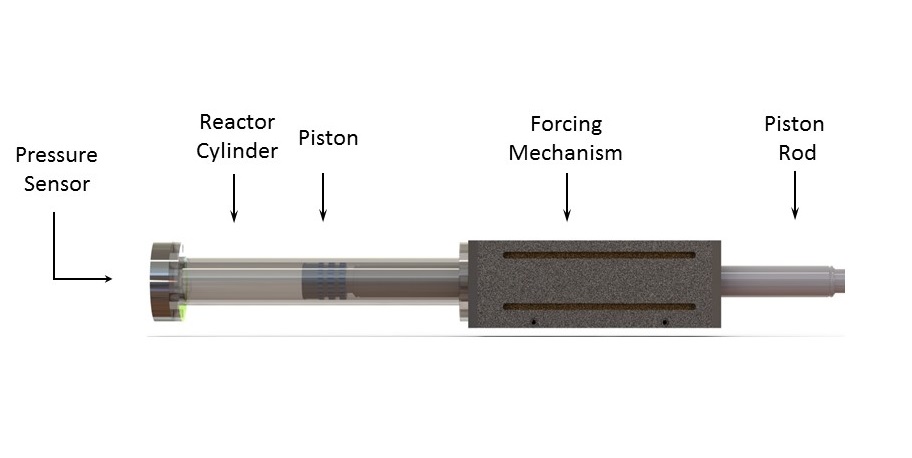
The high pressure and temperature conditions can be maintained for a duration of over 300 milliseconds in this RCEM. A simulation of an autoignition event in the compression mode is shown below.
Fuel Ignition Tester
Autoignition delay time is one of the fundamental combustion properties, which markedly differ for different types of commercial fuels. This property has conventionally been associated with the octane or cetane rating of a given fuel, and is generally used to assess the compatibility of the fuel with the intended end use in a reciprocating or rotary internal combustion engine. The FIT is a device that is used to obtain the cetane rating of fuels.